Poly – News
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
2022
März 3, 2022 T. B. Mrohs, O. Weichold Januar 19, 2022 Seit Januar unterstützt Nils Münstermann die Arbeitsgruppe im Bereich bio-basierte Baustoffe und entwickelt quellbare Chitosanderivate für Beton- und Agraranwendungen. Januar 4, 2022 O. Weichold VERSCHOBEN AUF 2023 Januar 3, 2022 O. Weichold VERSCHOBEN AUF 2023
Neue Veröffentlichung
Multivalent Allylammonium-Based Cross-Linkers for the Synthesis of Homogeneous, Highly Swelling Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride Hydrogels
Gels 2022, 8, 100 (open access)
Neuer Doktorand
Vortragsankündigung
Alkaline hydrogels – multifunctional materials for concrete rehabilitation – International Congress on Polymers in Concrete (IPCIC 2022)
Vortragsankündigung
Hochalkalische Hydrogele – die Schweizer Taschenmesser der Instandsetzung
NuBau – 5. Tagung Nutzerorientierte Bausanierung, Weimar.
2021
Dezember 20, 2021 M. Brenner, O. Weichold Dezember 8, 2021 Herzlichen Glückwunsch an Nils Münstermann zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Masterarbeit mit dem Titel „Synthese und Eigenschaften von Superabsorbern auf Basis von Chitosanhydrogelen“ im Studiengang Chemie! September 15, 2021 Die Veröffentlichung Alkaline hydrogels as ion-conducting coupling material for electrochemical chloride extraction von Andre Jung in Mater. Corr. hat es auf die Titelseite der Ausgabe 72 Band 9 geschafft! August 10, 2021 P. B. Sassmann, O. Weichold Juli 20, 2021 Am 1.10.2021 startet ein neues Projekt im Schwerpunkt bio-basierte Baustoffe. Auf Basis von Chitosan entwickeln wir zusammen mit zwei Industriepartnern Lasuren und Klebstoffe für Holz. Das Projekt wird von Tobias Boehnke betreut. Juli 14, 2021 Bericht aus dem laufenden Projekt Rissinjektion: O. Weichold Juli 14, 2021 Bericht aus dem abgeschlossenen Projekt Chloridentzug mit Gel: O. Weichold Mai 11, 2021 A. Jung, A. Faulhaber, O. Weichold Eine Veröffentlichung aus dem abgeschlossenen ZIM-Projekt „Chloridentzug mit Gel“ März 18, 2021 O. Weichold März 16, 2021 Bericht aus dem abgeschlossenen Projekt Chloridentzug mit Hydrogelen: O. Weichold März 12, 2021 Zur reproduzierbaren und qulatitativ hochwertigen Herstellung von Probekörpern und Mustern, z. B. aus unseren biobasierten Werkstoffen, haben wir eine Stepcraft M•1000 CNC-Fräse mit einem Arbeitsbereich von 679 × 1044 mm2 beschafft. Ansprechpartner ist Tobias Boehnke. März 10, 2021 Die Veröffentlichung Protein Hydrolysates from Biogenic Waste as an Ecological Flame Retarder and Binder for Fiberboards von Markus Brenner hat es auf die Titelseite der Ausgabe 5 Band 50 geschafft! Hier geht es zum Cover→ März 3, 2021 Rückwirkend zum 1.1. wurde uns ein Projekt zur Entwicklung in Wasser quellbarer Materialien aus Basis nachwachsender Rohstoffe bewilligt. Im Verbund mit industriellen Partnern werden der Zusammenhang zwischen Zusammensetzung und Eigenschaften aufgeklärt, Kapazitäten zum scale-up aufgebaut und geeignete Prototypen in der Endanwendungen getestet. Das Projekt wird von Tobias Boehnke betreut. März 3, 2021 Rückwirkend zum 1.11. wurde uns ein Projekt zur Entwicklung mechanisch stabiler Schäume bewilligt. Das Projekt baut auf die in Appl. Sci. 2020 beschriebenen
Neue Veröffentlichung
Poultry Feather Waste as Bio-Based Cross-Linking Additive for Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber
Polymers 2021, 13(22), 3908 (open access)
Masterarbeit abgeschlossen
Die Arbeit entstammt dem laufenden Projekt Biosuperabsorber.
Titelseite
Hier geht es zum Cover→
Neue Veröffentlichung
Synergistic effects in cross-linked blends of ion-conducting PEO-/PPO-based unsaturated polyesters
Ionics 2021, 27, 3857–3867 (open access)
Neues Projekt: Bio-basierte Lasuren und Klebstoffe für Holz
Vortrag
Acrylatfreie Zweikomponentengele zur Rissverpressung
7. Kolloquium „Erhaltung von Bauwerken“, Technische Akademie Esslingen, 14.7.2021, Ostfildern
Vortrag
Alkalische Hydrogele als Ankoppelungsmaterial für den elektrochemischen Chloridentzug
7. Kolloquium „Erhaltung von Bauwerken“, Technische Akademie Esslingen, 14.7.2021, Ostfildern
Neue Veröffentlichung
Alkaline hydrogels as ion-conducting coupling material for electrochemical chloride extraction
Matter. Corr. 2021, 72, 1448–1455 (open access)
Vortrag
Self-extinguishing wood-fibre boards using waste poultry-feather hydrolysates
1st International Conference on Science Technology & Innovation, 19.3.2021, Chiang Mai, Thailand
Vortrag
Electrochemical Chloride Extraction using diallyldimethylammonium hydroxide based hydrogels as electrolytes
3rd International Conference on the Chemistry of Construction Materials, 17.3.2021, Karlsruhe
Auf Touren gekommen
Titelseite
Neues Projekt: Biosuperabsorber
Neues Projekt: Recyclingschäume
Materialien auf. Zusätzlich wird die Wirkung von Füllstoffen aus
Recyclingmaterialien getestet. Das Projekt wird von Fabian
Weitenhagen betreut.
2020
Neuer Mitarbeiter
Dezember 22, 2020
Seit Dezember unterstützt Fabian Weitenhagen die Arbeitsgruppe im Bereich bio-basierte Baustoffe und entwickelt die ersten Arbeiten an den Polykondensationsharzen (Appl. Sci. 2020) weiter.
Neue Veröffentlichung
Dezember 18, 2020
M. Brenner, O. Weichold
Protein Hydrolysates from Biogenic Waste as an Ecological Flame Retarder and Binder for Fiberboards
ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32227 (open access).
Veröffentlichung
Oktober 6, 2020
A. Jung, M. B. Endres, O. Weichold
Polymers 2020
Zum Artikel→
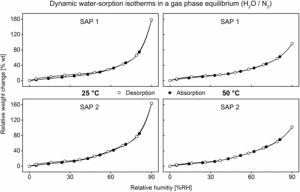
Influence of Environmental Factors on the Swelling Capacities of Superabsorbent Polymers Used in Concrete
ABSTRACT: Superabsorbent polymers (SAP) are of major interest as materials to control the cement hydration process. The swelling behavior of the SAPs significantly influences the performance of the resulting concrete by slowly releasing polymer-bound water in order to maintain a consistent w/c value. A round-robin test conducted by the RILEM Technical Committee 260-RSC showed that the same batch of polymer can lead to large deviations in concrete performance and this was assumed to originate in di
erent storage conditions of the SAP. In this contribution the change in the performance of two SAPs, a crosslinked poly(acrylate) and a crosslinked poly(acrylate-co-acrylamide), was assessed after ageing in standard climate, at 50
°C, and under UV irradiation. During storage in standard climate or 50 °C, ageing led to dehydration of the SAP, and this subsequently led to a higher water uptake during swelling. By contrast, UV irradiation reduced the water uptake, most likely as a result of photo-crosslinking. Dynamic water vapor sorption experiments indicated a strong dependence of the water uptake on both the ambient humidity and the temperature. As a result, cement mixtures containing SAP must be calculated on the dry mass of the SAP rather than the actual weight on site. A standard procedure of how to pack and handle SAP to be used in concrete is also provided.
Bachelorarbeit
September 4, 2020
Denis Clou
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit
Geflügelfedern als biobasierter Füllstoff in Elastomerlagern
Use of poultry feathers as a bio-based filler in elastomer bearings
Bachelorarbeit
September 3, 2020
Marvin Oomen
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit
Chitosanbasierte Interpolyelektrolytkomplexe zur Oberflächenversiegelung
Chitosan-based interpolyelectrolyte complexes for surface sealing
Veröffentlichung
Mai 5, 2020
M. Brenner, C. Popescu, O. Weichold
Appl. Sci. 2020
Zum Artikel→
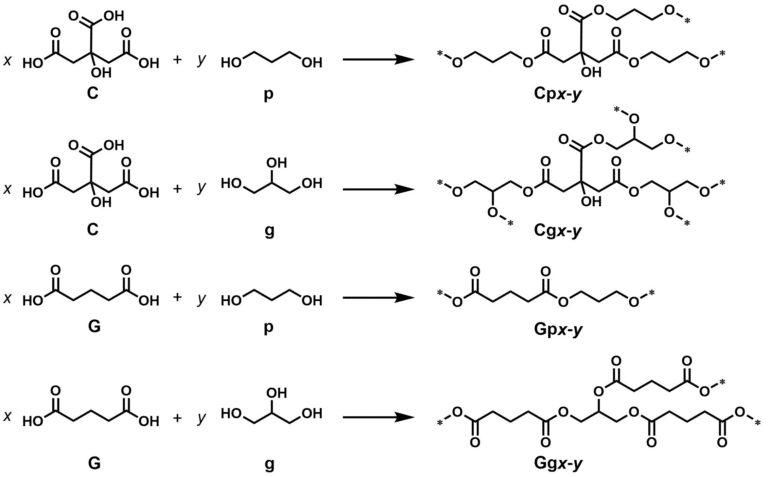
Anti-Frothing Effect of Poultry Feathers in Bio-Based, Polycondensation-Type Thermoset Composites
ABSTRACT: The formation of polycondensation-type thermoset resins from natural reactants such as citric and glutaric acid, as well as 1,3-propanediol and glycerol, was studied. Monitoring the mass loss by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) allowed the rate constants of the esterification to be calculated, which were in the order of 7·10−5 s−1 for glutaric acid and approximately twice as high for citric acid. However, the combination citric acid/glycerol was previously reported to froth up at high conversions, giving rise to foams, which makes the preparation of compact engineering composites challenging. In light of this, we observed that shredded poultry feathers not only increased the conversion and the reaction rate of the combination citric acid/glycerol, but increasing the amount of feathers continuously decreased the number of visible bubbles. The addition of 20 wt% of feathers completely prevented the previously reported frothing and gave rise to compact materials that were macroscopically free of defects. Besides this, the addition of feathers also improved the fire-retardant properties. The tensile properties of the first specimens are still rather low (σ = 11.6 N/mm2, E = 750 N/mm2), but the addition of poultry feathers opens a new path for green thermoset resins.
Masterarbeit
Februar 3, 2020
Tim Mrohs
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Masterarbeit
Synthese von vernetzten Copolymerelektrolytgelen auf Basis von Diallyldimethylammoniumchlorid und -hydroxid
Synthesis of crosslinked copolymer electrolyte gels based on diallyldimethylammonium chloride and -hydroxide
2019
Oktober 1, 2019 O. Weichold, P. B. Sassmann Jahrestagung der GDCh-Fachgruppe Bauchemie, 1.10.2019, Aachen Numerische Strukturanalyse für das in silico Design moderner Hybridmaterialien ABSTRACT: Oktober 1, 2019 M. Brenner Jahrestagung der GDCh-Fachgruppe Bauchemie, 1.10.2019, Aachen Einsatz von Federkeratin als Brandschutzimprägnierung für Holz und als nicht brennbares Wärmedämmmaterial ABSTRACT: August 13, 2019 Kaja Kensmann Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit August 5, 2019 Sarah Weides Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit Juni 3, 2019 O. Weichold European Polymer Congress, 13. Juni 2019, Kreta Fighting fire with feathers – transforming natural waste into flame-retardant materials ABSTRACT: Januar 16, 2019 T. Juraschek, O. Weichold Elektrochromie zur Visualisierung kleiner Strommengen ABSTRACT: Januar 16, 2019 C. Morales Cruz, Oliver Weichold, H.-J. Kocks FOULPROTECT – zur Problematik des Bewuchses in Meerwasserbauwerken ABSTRACT: Januar 14, 2019 P. B. Sassmann, O. Weichold Preparation ABSTRACT:
Vortrag
Moderne Hochleistungsmaterialien erhalten ihre außergewöhnlichen
Eigenschaften aus dem Zusammenspiel einzelner Komponenten. Aus
mechanischer Sicht ergeben sich jedoch Probleme bei der Bestimmung des
makroskopischen Materialverhaltens. Ziel ist demnach die Ermittlung des
Materialverhaltens durch numerische Simulation am Beispiel eines
polymergetränkten Betonkörpers.
Vortrag
Es werden neue Verwendungsmöglichkeiten für Federn gezeigt, da diese
als biogener Reststoff in großen Mengen anfallen. Dabei ist die
Verbesserung der Brandeigenschaften ein zentraler Punkt. Die Federn
werden einerseits zu einer nicht brennbaren Wärmedämmplatte verarbeitet.
Außerdem werden keratinhaltige Lösungen zur Behandlung von
Holzwerkstoffen genutzt um gezielt die Brennbarkeit zu verringern und
das Glimmverhalten zu verbessern.
Bachelorarbeit
Thermoplastische Verarbeitung von Federn mit einem polymerisierbaren Weichmachersystem
Thermoplastic treatment of feathers with a polymerizable plasticizer system
Bachelorarbeit
Synthese und elektrochemische Charakterisierung von Oligoethylenglykol-modifizierten 4,4′-Bipyridinen
Synthesis and electrochemical behaviour of oligoethyleneglycol-modified 4,4′ bipyridines
Vortrag
Keratin is a natural fibre protein widely found in the animal kingdom,
where it is the basis of e. g. wool and hair, horns, scales, and
feathers. Besides its broad spectrum of mechanical properties, keratin
is particularly characterized by its poor flammability and even
self-extinguishing behaviour. Most approaches which use keratin as a
chemical feedstock require a solubilisation step, and this can be
accomplished by either alkaline hydrolysis or reduction of the
disulphide bridges. We have refined the latter to be more convenient and
economical, but more importantly to produce two kreatin fractions,
which were both found to be valuable intermediates in producing
flame-retarding materials. The first fraction consists of water-soluble
protein hydrolysates, which can be used as impregnation for particle and
fibre boards. The second fraction is a gel, which can be transformed
into foamed boards. These materials match commercial EPS/XPS boards in
terms of their thermal conductivities, but will not ignite or burn when
subjected to an open flame. The contribution will present our latest
results on the preparation and application of these two fractions.
Veröffentlichung
Beton 2019, 5, 168–171.
Ein Nachteil aktueller Korrosions-Monitoringsysteme ist die
Verfügbarkeit geeigneter Auslesegeräte zur Prognose der Lebensdauer der
überwachten Strukturen. Vor Ort installierte, wartungsfreie und einfach
abzulesende Einheiten wären für den Einsatz von Vorteil. Vor diesem
Hintergrund wurde ein Bauteil entwickelt, das in der Lage ist, kleine
Strommengen auf Basis der Elektrochromie zu visualisieren. Ziel ist es
in erster Linie, Korrosionsströme zu erfassen und visuell entsprechend
darzustellen. In dem Beitrag werden der Aufbau des Bauteils, seine
elektrochemische Charakterisierung und die Visualisierung von
Korrosionsströmen unter Laborbedingungen sowie an real korrodierenden
Stahlbetonprüfkörpern beschrieben.
Veröffentlichung
Beton 2019, 5, 162–167.
Im Rahmen des Verbundprojekts FOULPROTECT „Bewuchsschutz und Vermeidung
von Biokorrosion in der Maritimen Technik“ wurde am Institut für
Bauforschung der RWTH Aachen University (ibac) in Zusammenarbeit mit den
Firmen Salzgitter Mannesmann Line Pipe GmbH (SMLP) und LimnoMar eine
mineralische Ummantelung mit erhöhtem mechanischen Widerstand für
Stahlkonstruktionen im Meerwasserbereich entwickelt. Die Eignung
verschiedener kommerziell verfügbarer Werktrockenmörtel als
Schutzschicht wurde am Beispiel von Stahlrohren für Gründungsstrukturen
von Offshore-Windkraftanlagen getestet. Dazu wurden die Frisch- und
Festmörtelkennwerte bestimmt sowie Dauerhaftigkeitsuntersuchungen in
Laborversuchen unter realen Bedingungen (Luft- und Meerwasserlagerung)
durchgeführt. Der Aufwuchs (Biofouling) auf der Mörtelumhüllung bei
einer Meerwasserlagerung konnte bei keinem der untersuchten Materialien
verhindert werden, aber fluoreszenzmikroskopische Untersuchungen zeigten
weder Mikro- noch Makrobesiedlungen unterhalb der Mörteloberfläche.
Zwischen den einzelnen Materialien wurden deutliche Unterschiede bei der
Rissanzahl der ausgelagerten Proben festgestellt. Unter
Berücksichtigung aller Untersuchungen weisen hochfeste Mörtelmischungen
das größte Potenzial auf, abrasiven Einwirkungen und inneren
Sprengdrücken dauerhaft standzuhalten.
Veröffentlichung
Ionics 2019
Zum Artikel→
and characterisation of ion-conductive unsaturated polyester resins for
the on-site production of resistivity sensors
Ion-conductive unsaturated polyesters were synthesised from
poly(ethylene oxide) and maleic anhydride for use in the development of
improved methods for the structural-health monitoring of infrastructural
buildings. The unsaturated polyesters (UP) were cross-linked with
styrene using a redox initiator in the presence of LiClO4.
Electrochemical impedance-spectroscopy was used to study the effects of
initiator and styrene concentration as well as the EO:Li+ ratio.
Increasing the initiator or styrene content results in an increased
resistivity of the final materials. Cross-linking with styrene does not
appear to cause microphase separation into pure UP and polystyrene
phases, since the resulting resistivities are significantly lower than
predicted by the rule of mixtures. For all temperatures under
investigation (0 °C to 60 °C), the lowest resistivities were found for a
EO:Li+ ratio of 50 (400 Ω·m at 22 °C), which is in accordance with
previous findings. The electrical properties of the present materials
are determined by diffusion controlled process in such a way
polarisation prevails at high temperatures. In a proof of principle
experiment, one selected UP formulation was injected into drill holes in
concrete and cured at different temperatures and moisture conditions.
This system reliably monitors the resistivity against an embedded
reference electrode.
2018
November 20, 2018 M. B. Endres, O. Weichold Sorption-active transparent films based on chitosan ABSTRACT:
Veröffentlichung
Carbohydrate Polym. 2018
Zum Artikel→
In this paper we describe the preparation of alkanoic acid-based
aqueous chitosan solutions, which show no sign of acid-catalysed
depolymerisation over time – something commonly accompanying other
preparation methods. Longer chitosan chains have previously been shown
to exhibit more advantageous biological activities, and constant
viscosities are essential for consistent quality in biomedical
applications. Avoiding acid-catalysed depolymerisation requires careful
control of the stoichiometry between the free amino groups of chitosan
and the appropriate solubilising acid. Acetic and butyric acid are both
suitable solubilising agents, but chitosan butyrate exhibits lower
solution viscosities due to a combined electric and steric shielding of
the chains.
These solutions dry into clear transparent films that
remain fully water soluble and absorb up to 70 wt% of water from 90 %-RH
vapour phase at 25 °C. The absorption follows simple first-order
kinetics and the rate constants increase with increasing humidity up to
approx. 71 %-RH, where a metastable chitosan trihydrate salt appears to
be formed. Desorption is slightly faster, but more complex, as it
exhibits two distinct first-order processes. In addition, films prepared
in this way are thermally more stable than the usual chitosan
hydrochloride.

Titelseite
Oktober 16, 2018
A. Jung, O. Weichold
Andres Veröffentlichung „Preparation and characterisation of highly alkaline hydrogels for the re-alkalisation of carbonated cementitious materials“ wurde von Soft Matter für die Gestaltung der Titelseite ausgewählt
Bachelorarbeit
Oktober 3, 2018
Lutz Burow
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit
Untersuchung der thermischen Eigenschaften von mit Keratin imprägnierten Holzspänen
Thermal properties of keratin-impregnated chipped wood
Vortrag
September 11, 2018
O. Weichold
IBAUSIL, Weimar, 12.–14. September 2018
Polymere und Beton – Eine wilde Ehe mit Potential
Bachelorarbeit
September 3, 2018
Lena Schmitz
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit
Vernetzte Polyethylenglycole als Träger für ionenleitfähige Filme
Cross-linked polyethylene glycol matrix for ion-conductive films
Masterarbeit
August 14, 2018
Jan Tenbusch
Diese Masterarbeit wurde extern, in Zusammenarbeit mit der Fa. Henkel durchgeführt. Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss.
Bachelorarbeit
August 7, 2018
Kathrin Dahm
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit
Synthese ethoxylierter und propoxylierter Styrole zur Herstellung ionisch leitfähiger Polyester
Synthesis of ethoxylated and propoxylated styrene for the formation of ionic conductive polyesters
Bachelorarbeit
Juli 3, 2018
Julia Littke
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit
Synthese ungesättigter Polyester auf Basis von PPO
Synthesis of unsaturated polyesters based on PPO
Veröffentlichung
Mai 9, 2018
A. Jung, O. Weichold
Soft Matter. 2018
Zum Artikel→
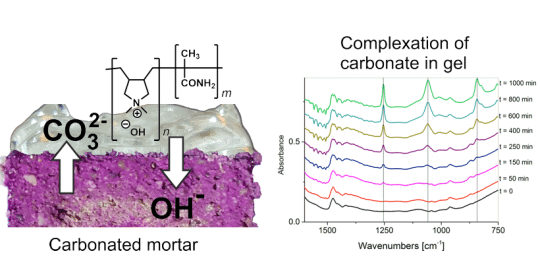
Preparation and characterisation of highly alkaline hydrogels for the re-alkalisation of carbonated cementitious materials
ABSTRACT:
Highly alkaline hydrogels that allow the restoration of alkaline buffer
in cementitious materials can be obtained from diallyldimethylammonium
hydroxide. The latter must be prepared in dilute solutions and
polymerised at ambient temperatures in order to avoid decomposition.
Using methacrylamide as a neutral co-monomer capable of forming hydrogen
bonds, the rheological properties of the gels can be adjusted over a
wide range; e.g. the viscosity increases a thousandfold from 0.35 Pa·s
to 4350 Pa·s by using 10 mol% methacrylamide. For the proof of principle
experiments, gels with 9 mol% methacrylamide were used, which contain
approx. 1.6 mol hydroxide ions per kg gel. Ion exchange between this and
a neutral chloride containing gel provided an apparent diffusion
coefficient of 4.12·10−7 m2 s−1 for the hydroxide ions and confirmed the
transport of chloride ions into the alkaline gel. The re-alkalisation
was tested on fully carbonated mortar prisms made from Portland cement.
Re-alkalisation of the mortar was confirmed by the phenolphthalein test
according to DIN EN 14630:2007-01 and by a control experiment with pure
calcium carbonate using IR spectroscopy.
Bachelorarbeit
April 3, 2018
Jan Bandowski
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit
Entwicklung von Steuerungsmechanismen zur Regulierung der viskosen Eigenschaften eines PolyDADMAC-Gels
Development of mechanisms to control the viscous properties of PolyDADMAC gels
Die Arbeit wurde zusammen mit der FH Aachen, Fachbereich Chemie und Biotechnologie durchgeführt.
2017
Oktober 3, 2017 T. Juraschek, O. Weichold Development ABSTRACT: September 19, 2017 M. Brenner Funktionalisierung von Faseroberflächen für textilbewehrte Elastomere ABSTRACT: September 19, 2017 O. Weichold Tagung der GDCh-Fachgruppe Bauchemie, Weimar, 19. September 2017 Polymere im Bauwesen – weiche Materialien in einer harten Welt September 4, 2017 O. Weichold, U. Antons Assessing the Performance of Hydrophobing Agents on Concrete using Non-Destructive Single-Sided Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ABSTRACT: September 3, 2017 T. Juraschek Chemical, Non-Electronic Corrosion Indication Systems ABSTRACT: Juli 1, 2017 Unsere Ehemalige Elena Heß tritt zum 1.7.2017 eine Stelle bei HeidelbergCement an. Juni 7, 2017 R. Schulte Holthausen, O. Weichold Non-destructive Evaluation of Thermal Damage in Concrete by Single-Sided Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ABSTRACT: Juni 3, 2017 Iva Rroshi Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit März 3, 2017 Markus Brenner Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Masterarbeit
Veröffentlichung
J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2017; e3739
Zum Artikel→
of an electrochromic device triggered by the macrocell current in
chloride-induced corrosion of steel-reinforced concrete
This article presents the development and characterisation of an
electrochromic device and its application to detect steel corrosion in
reinforced concrete. Steel corrosion inflicts an enormous annual
economic damage, which could be reduced by the installation of
appropriate monitoring devices. These should be simple, reliable, long
lasting, and should not require service or maintenance. The present
electrochromic device is constructed in such a way that it uses the
macrocell current in an active, chloride‐induced corrosion element as
power supply to trigger the colour change. This way, the system stays
inactive until corrosion occurs. The device consists of diheptyl
viologen in a liquid polymer electrolyte made from LiClO4 and
poly(ethylene glycol) with Mw = 400 g mol−1. The addition of viologen
lowers the resistance but causes no further changes in the
electrochemical properties of the polymer electrolyte. Impedance spectra
indicate ion transport rather than capacitance effects to dominate the
electrochemical properties. Experiments using direct current in the
microampere range show electrochromic switching times of several
minutes, which is sufficient for the intended monitoring application.
Vortrag
Tagung der GDCh-Fachgruppe Bauchemie, Weimar, 19. September 2017
Maßgeblich für die Tragfähigkeit von textilbewehrten Strukturen ist die
Leistungsfähigkeit der Grenzfläche. In zementgebundenen Systemen wird
dies meist durch formschlüssige Verbindungen (z. B. mit Epoxidharz
getränkte und abgesandete Carbontextilien) erreicht. In polymeren
Materialien ist ein derart steifer Verbund auf Grund der kleineren
E-Moduln häufig unerwünscht, bei Elastomeren sogar kontraproduktiv.
Der
Vortrag berichtet über eine Untersuchung zur gezielten chemischen
Funktionalisierung von Glas-, Basalt- und Carbonfasern zur Verstärkung
von Chloropren und EPDM. Die Fasern wurden jeweils mit
Bis[3-(triethoxysilyl)propyl]tetrasulfid (TESPT) und
3-(Mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilan (3-MPTMS) modifiziert. Zur Applikation
wurden die Substanzen mit gelöstem Elastomer versetzt und händisch auf
die Fasern aufgetragen. Anschließend wurden die modifizierten Fasern in
einer speziell gefertigten Form ins Elastomer einvulkanisiert und die
Faser-Matrix-Adhäsion per Ausziehversuch getestet. Bei Glas- und
Basaltfasern konnte eine Verbesserung des Verbunds um bis zu ca. 100 %
erreicht werden, bei der Modifikation von Carbonfasern lässt sich der
Verbund um ca. 50 % verbessern.
Vortrag
Veröffentlichung
J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2017, 23, 04017010
Zum Artikel→
Single-sided nuclear magnetic resonance is a nondestructive analytical
technique by which the ingress behavior of hydrophobing agents as well
as the properties and performance of the resulting hydrophobic layers
can be assessed quantitatively. The method is used to compare the
behavior of two low-molecular-weight hydrophobing agents,
n-octyltriethoxysilane and i-butyltriethoxysilane, on concrete and to
assess the properties of the resulting hydrophobic layers. For the octyl
derivative, ingress appears to be a simple transport process without
pronounced polycondensation in the liquid phase or reaction with the
pore walls because the detectable amount stays rather constant during
the first day of observation. In addition, the thickness of the
resulting hydrophobic layer correlates well with the endpoint of the
transport process. In contrast, the detectable amount of the butyl
derivative is reduced to half during the first 18 h, indicating either
substantial polycondensation or anchoring to the pore walls, and the
hydrophobic layer is approximately 25% thicker than indicated by the
ingress profiles. The different behavior could originate in differences
in the molecular structure, particularly the steric demand of the alkyl
substituents, although this requires a more detailed study. Both
compounds proved to be excellent hydrophobing agents since the layers
were found to be impermeable when kept in a shallow water bath
(unidirectional transport through the layer) for more than 1 year. The
results demonstrate that single-sided nuclear magnetic resonance is an
excellent nondestructive tool for quality assurance when applying such
protective layers.
Vortrag
EUROCORR 2017, Prag, 3. September 2017
Corrosion of the steel reinforcement in concrete causes an enormous
economic damage. In particular, chloride-induced macroelement corrosion
of the reinforcement is one of the bottlenecks in the service life time
design of a majority of infrastructure buildings with a significant
exposition to chloride. Corrosion monitoring offers a possibility to
detect the onset of corrosion events and start independent restoration
actions at a point, where costs can be kept at a minimum.
The
presentation focusses on the testing procedure and verification of the
prototype, under conditions simulating real-life corrosion events. Color
change is not observed when applying zero-load currents, but occurs
within minutes after raising either the potential or current to levels
typical for corrosion events. The color change is persistent even after
turning the power source off. We applied potential controlled current
profiles as well as voltage controlled current profiles to the device,
also with respect to peak current profiles to show the response of the
system under realistic circumstances. Also, we investigate the influence
of zero-load current and voltage events during the passive state of the
reinforcement steel after passivation. Furthermore, experiments on
reinforcement steel and reinforced concrete samples are shown as a
proof-of-principle experiment.
Karriere
Veröffentlichung
J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2017, 23, B4016006.
Zum Artikel→
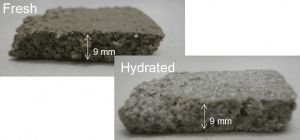
A new technology to coat concrete with coherent layers of glass by
flame-spraying is currently developed at the Institutes of Building
Materials Research and Mineral Engineering of RWTH Aachen University in
Germany through a joint program. A major factor influencing the pull-off
strength of the flame-sprayed glass coating is thermally induced damage
in the underlying concrete substrate. In this article, the authors
present a nondestructive test method using single-sided 1H nuclear
magnetic resonance (NMR) to evaluate the thermally induced damage in
concrete specimens. The particular NMR device used in this project
primarily detects water and can qualitatively assess the water content
as well as the relative size of water-filled voids such as pores and
cracks. To do so, the specimens are water saturated and subsequently
analyzed by NMR. Changes in the NMR-signal are interpreted in terms of
change in porosity and development of cracks inside the cement stone as a
function of depth from the concrete surface.
Bachelorarbeit
Zur Untersuchung der Genauigkeit bei der Ermittlung des Bindemittelgehalts an Betonproben durch Methoden der chemischen Analytik
Investigation
of the accuracy conerning the determination of the binder content of
concrete samples by methods of analytical chemistry
Masterarbeit
Funktionalisierung von Faseroberflächen für textilbewehrte Elastomerlager
Functionalization of Fiber Surfaces for Textile-Reinforced Elastomeric Bearings
Vortrag
Januar 25, 2017
O. Weichold
Seminar „Stadtstraßen / Ortsdurchfahrten“ des VSVI Niedersachsen e.V., ABZ Mellendorf, 25. Januar 2017
CARPET – Konfektionierter, aufrollbarer, polymerbasierter Straßenbelag
Konferenzbeitrag
Januar 10, 2017
T. Juraschek, O. Weichold
6th International Conference on Concrete Repair (Concrete Solutions), Thessaloniki, 2017, S. 207–211.
In-situ methods of detecting steel corrosion using permanent and non-electronic systems
ABSTRACT:
Current systems for detecting corrosion of the reinforcement in
concrete are realized via highly specialized systems that are
commercially not available. Thus, these systems require complete
technical support by the installing company. This report shows a cheap,
efficient, independent, and reliable method to detect corrosion events
in concrete. The detection system is based on an electrochromic device,
which changes its colour upon the change of electrochemical potential
caused by the corrosion process. The device is realized by a
layer-by-layer setup of a transparent electrode, e. g. indium-doped tin
oxide (ITO), followed by an electrochromic layer. The system is closed
by a metal counter electrode. The electrochromic layer can consist of an
electrochromic compound in a conducting polymer system. By connecting
such elements to a series of sensors, e. g. an anode ladder, it is
possible to monitor the corrosion progress and to verify the service
life design of a structure.
Konferenzbeitrag
Januar 10, 2017
P. B. Sassmann, O. Weichold
6th International Conference on Concrete Repair (Concrete Solutions), Thessaloniki, 2017, S. 235–238.
Development
of Electrically Conductive Resins for the On-Site Fabrication of
Sensors for Corrosion Detection and Risk Assessment in Reinforced
Concrete
ABSTRACT: Assessing the risk of corrosion in
steel-reinforced concrete can be accomplished using different types of
sensors such as anode ladders or multi-ring electrodes. The former are
unsuitable for retrofit installations, while the latter require the use
of embedding mortars to achieve conductive connections with the
surrounding concrete. However, the porosity of the embedding mortar
differs from that of the concrete and the retrofitting action introduces
additional moisture. This interferes with resistivity and/or potential
measurements and makes interpretations of the actual situation
problematic. To circumvent these disadvantages, we have developed a
liquid reactive polymer resin with high electrical conductivity that can
be used to fabricate sensors directly inside drill holes. The mixture
solidifies in a short time and its adhesive properties provide an
excellent conductive connection to the concrete walls. The resin
contains no water so that reliable values can be obtained immediately
after solidification. By changing the additives both resistivity and
potential sensors can be obtained. The mixture is cheap so that large
sensor networks can be installed at reasonable costs. Such networks are
ideal for the precise localization of corrosion events and more
importantly for risk assessment in steel-reinforced structures.
2016
Vortrag
Dezember 2, 2016
O. Weichold
nuBau – 3. Tagung Nutzerorientierte Bausanierung, Weimar, 30. November – 1. Dezember 2016
Neue Methoden zur Auswertung von Sw-ρ-Beziehungen
ABSTRACT:
Der spezifische elektrische Widerstand des Betons wird häufig
herangezogen, um Aussagen über die Dauerhaftigkeit von
Stahlbetonbauwerken zu treffen. Das Ziel der vorgestellten
Untersuchungen besteht darin, Wassergehalt-Widerstandsbeziehungen in
Abhängigkeit von relevanten Strukturparameten des Betons zu
charakterisieren. Hierzu wurde ein Ansatz auf Basis von Archies Gesetz
gewählt, dessen Ergebnisse vorgestellt und mit dem üblicherweise
velwendeten Modell verglichen werden. Es wird versucht, ausgewählte
Parameter mit den Eigenschaften des Porensystems der Betone zu
konelieren und so die Möglichkeiten des vorgestellten Ansatzes
aufzuzeigen.
Vortrag
Oktober 12, 2016
P. B. Sassmann
2nd International Conference on the Chemistry of Construction Materials (ICCCM), München, 10.–12. Oktober 2016
Development of ion- conductive polymer resins for the on-site fabrication of corrosion sensors
ABSTRACT:
Assessing the corrosion risk in steel-reinforced concrete can be
accomplished by implementing monitoring systems. For retrofit
installations the electrically conductive connection of sensors and
surrounding concrete is currently realised with cement-based embedding
mortars. The use of such aqueous systems changes the moisture content of
the concrete close to the sensor, which interferes significantly with
resistivity and/or potential measurements and makes interpretations of
the measured values problematic.
To circumvent these disadvantages,
we developed a liquid, reactive, non-aqueous polymer resin with high
electrical conductivity that can be used to fabricate sensors directly
inside drill holes. This way, a close contact between sensor and the
concrete walls is automatically provided. Since the polymer resin is not
aqueous, the moisture balance of the old concrete is not altered so
that reliable values can be obtained immediately after solidification.
Buchbeitrag
Mai 20, 2016
J.-P. Lecomte, O. Weichold
in Y. Liu (Ed.), Silicone Dispersions (Surfactant Science Series Vol. 159), CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2016, S. 301–331.
Silane-based Water Repellents for Inorganic Construction Materials
Masterarbeit
Mai 2, 2016
Pia B. Sassmann
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Masterarbeit
Ionenleitende ungesättigte Polyester zur Ankopplung von Zulagekathoden in Beton
Ion-conductive unsaturated polyester for contacting galvanic couples in concrete
Veröffentlichung
April 2, 2016
D. Heinze, Th. Mang, C. Popescu, O. Weichold
Thermochim. Acta 2016, 637, 143–153
Zum Artikel→
Effect
of side chain length and degree of polymerization on the decomposition
and crystallization behaviour of chlorinated poly(vinyl ester) oligomers
ABSTRACT:
Four members of a homologous series of chlorinated poly(vinyl ester)
oligomers CCl3–(CH2CH(OCO(CH2)mCH3))n–Cl with degrees of polymerization
of 10 and 20 were prepared by telomerisationusing carbon tetrachloride.
The number of side chain carbon atoms ranges from 2 (poly(vinyl acetate)
to 18 (poly(vinyl stearate)). The effect of the n-alkyl side chain
length and of the degree of polymerizationon the thermal stability and
crystallization behaviour of the synthesized compounds was
investigated.All oligomers degrade in two major steps by first losing
HCl and side chains with subsequent breakdownof the backbone. The
members with short side chains, up to poly(vinyl octanoate), are
amorphous andshow internal plasticization, whereas those with high
number of side chain carbon atoms are semi-crystalline due to side-chain
crystallization. A better packing for poly(vinyl stearate) is also
noticeable.The glass transition and melting temperatures as well as the
onset temperature of decomposition areinfluenced to a larger extent by
the side chain length than by the degree of polymerization.
Thermalstability is improved if both the size and number of side chains
increase, but only a long side chaincauses a significant increase of the
resistance to degradation. This results in a stabilization of PVAc
sothat oligomers from poly(vinyl octanoate) on are stable under
atmospheric conditions. Thus, the way todesign stable, chlorinated PVEs
oligomers is to use a long n-alkyl side chain.
Bachelorarbeit
April 2, 2016
Tim Kurschildgen
Wir gratulieren zum erfolgreichen Abschluss der Bachelorarbeit
Einfluss der Copolymerisation funktioneller Monomere im Porenraum auf die mechanischen Eigenschaften von Mörtel
Copolymerisation of functional monomers in the pore system of mortars and its influence on the mechanical properties
Zurück zum Forschungsfeld Polymere Materialien →

